Direct Subsidized and Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans are federal student loans offered by the U.S. Department of Education (ED) to help eligible students cover the cost of higher education at a four-year college or university, community college, or trade, career, or technical school. (You might see Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans referred to as Stafford Loans or Direct Stafford Loans, but these aren’t the official loan names.)
Differences Between Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans
In short, Direct Subsidized Loans have slightly better terms to help out students with financial need.
Quick Overview of Direct Subsidized Loans
Who can get Direct Subsidized Loans?
Direct Subsidized Loans are available to undergraduate students with financial need.
How much can you borrow?
Your school determines the amount you can borrow, and the amount may not exceed your financial need.
Who will pay the interest?
The U.S. Department of Education pays the interest on a Direct Subsidized Loan
while you’re in school at least half-time,
for the first six months after you leave school (referred to as a grace period*), and
during a period of deferment (a postponement of loan payments).
Quick Overview of Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Who can get Direct Unsubsidized Loans?
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to undergraduate and graduate students; there is no requirement to demonstrate financial need.
How much can you borrow?
Your school determines the amount you can borrow based on your cost of attendance and other financial aid you receive.
Who will pay the interest?
You are responsible for paying the interest on a Direct Unsubsidized Loan during all periods.
Good to know
During periods of time when you are not required to make payments—such as while you are in school, in a deferment, or in a forbearance—your interest will accrue (accumulate) and it will in certain instances be capitalized (which means that your interest will be added to the principal amount of your loan). Whether your unpaid interest capitalizes or not, you are still responsible for paying the interest that accrues. You can always choose to pay the interest that accrues even when you are not required to make a payment.
When does unpaid interest capitalize?
Loan Amount Limits
Your school determines the loan type(s), if any, and the actual loan amount you are eligible to receive each academic year. However, there are limits on the amount in subsidized and unsubsidized loans that you may be eligible to receive each academic year (annual loan limits) and the total amounts that you may borrow for undergraduate and graduate study (aggregate loan limits). The actual loan amount you are eligible to receive each academic year may be less than the annual loan limit. These limits vary depending on:
what year you are in school and
whether you are a dependent or independent student.
The following chart shows the annual and aggregate limits for subsidized and unsubsidized loans.
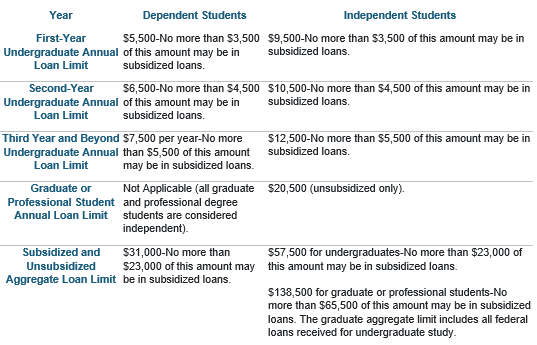
Notes:
The graduate aggregate limit includes all federal loans received for undergraduate study.
The aggregate loan limits include any Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans or Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans you may have previously received under the Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program. As a result of legislation that took effect July 1, 2010, no further loans are being made under the FFEL Program.
Effective for periods of enrollment beginning on or after July 1, 2012, graduate and professional students are no longer eligible to receive Direct Subsidized Loans. The $65,500 subsidized aggregate loan limit for graduate or professional students includes subsidized loans that a graduate or professional student may have received for periods of enrollment that began before July 1, 2012, or for prior undergraduate study.
If the total loan amount you receive over the course of your education reaches the aggregate loan limit, you are not eligible to receive additional loans. However, if you repay some of your loans to bring your outstanding loan debt below the aggregate loan limit, you could then borrow again, up to the amount of your remaining eligibility under the aggregate loan limit.
Who is Eligible
To receive either type of loan, you must be enrolled at least half-time at a school that participates in the Direct Loan Program. Generally, you must also be enrolled in a program that leads to a degree or certificate awarded by the school. Direct Subsidized Loans are available only to undergraduate students who have financial need. Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to both undergraduates and graduate or professional degree students. You are not required to show financial need to receive a Direct Unsubsidized Loan.
How to Apply
To apply for a Direct Loan, you must first complete and submit the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA®) form. Your school will use the information from your FAFSA form to determine how much student aid you are eligible to receive. Direct Loans are generally included as part of your financial aid package.
Loan Interest Rates and Fees
What are the current interest rates?
What are the loan fees?
Steps to Accept a Loan
If your financial aid package includes federal student loans, your school will tell you how to accept the loan.
If it is your first time receiving a Direct Loan, you will be required to
complete entrance counseling, a tool to ensure you understand your obligation to repay the loan; and
sign a loan contract called a Master Promissory Note, agreeing to the terms of the loan.
Contact the financial aid office at the school you are planning to attend for details regarding the process for receiving a loan at your school.
How Funds are Delivered
The school will first apply your loan funds to your school account to pay for tuition, fees, room and board, and other school charges. If any additional loan funds remain, they will be returned to you. All loan funds must be used for your education expenses. Learn more about the process of receiving federal student aid.
Loan Servicer’s Role
When you receive your Direct Loan, you will be contacted by your loan servicer (you repay your loan to the loan servicer). Your loan servicer will provide regular updates on the status of your Direct Loan, and any additional Direct Loans that you receive.
After you graduate, leave school, or drop below half-time enrollment, you will have a six-month grace period before you are required to begin repayment. During this period, you'll receive repayment information from your loan servicer, and you'll be notified about your first payment due date. Payments are usually due monthly. Learn more about repaying your loan.
Loan Repayment
After you graduate, leave school, or drop below half-time enrollment, you will have a six-month grace period before you are required to begin repayment. During this period, you'll receive repayment information from your loan servicer, and you'll be notified of your first payment due date. Payments are usually due monthly. Learn more about repaying your loan.
Loan Repayment Plans
There are several repayment options available that are designed to meet the individual needs of borrowers. Your loan servicer can help you understand which repayment options are available to you. Generally, you’ll have 10 to 25 years to repay your loan, depending on the repayment plan that you choose. Learn more about your repayment options.
Loan Deferment and Forbearance
If you are unable to make your scheduled loan payments, contact your loan servicer immediately. Your loan servicer can help you understand your options for keeping your loan in good standing. For example, you may wish to change your repayment plan to lower your monthly payment or request a deferment or forbearance that allows you to temporarily stop or lower the payments on your loan. Learn more about deferment or forbearance options.
How to Cancel a Loan
Before your loan money is disbursed, you may cancel all or part of your loan at any time by notifying your school. After your loan is disbursed, you may cancel all or part of the loan within certain time frames. Your promissory note and additional information you receive from your school will explain the procedures and time frames for canceling your loan.
Loan Forgiveness or Discharge
Under certain conditions, you may be eligible to have all or part of your loan discharged or forgiven (canceled). Find out about loan cancellation, discharge, or forgiveness.
Find Your Student Loan Information
Visit “My Aid” to view information about all of the federal student loans and other financial aid you have received and to find contact information for the loan servicer for your loans.
